Introduction
In the realm of technology, few stories are as remarkable and inspiring as that of Apple Inc. What started as a small venture in a humble garage would ultimately blossom into a global phenomenon, reshaping industries and redefining the way we live, work, and communicate. Join us as we embark on a journey through the fascinating history of Apple Inc., tracing its extraordinary rise from a garage startup to a force to be reckoned with in the tech world.
Genesis of Apple Inc.
1.1 The Founding Team Apple Inc.
In a start, Apple was founded by Steve Jobs with his colleague Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne in 1976. Jobs, the visionary leader, brought a passion for design and user experience, while Wozniak, the brilliant engineer, brought technical expertise. Wayne, who would later sell his shares, played a brief role in the company’s early days.
1.2 Vision and Mission From the beginning,
Apple had a vision to create user-friendly computers that would make technology accessible to everyone. Jobs and Wozniak believed that technology should be intuitive, beautifully designed, and capable of transforming people’s lives.
1.3 The Birth of the Apple I In 1976,
Apple introduced its first product, the Apple I. Designed by Wozniak, it was a bare circuit board that required users to connect their own keyboard, monitor, and power supply. While the Apple I had limited commercial success, it laid the foundation for future innovations.
2. The Breakthrough: The Apple II and Macintosh Era
2.1 Apple II:
A Game-Changing Computer In 1977, Apple released the Apple II, a complete personal computer with a built-in keyboard, color graphics, and expansion slots. The Apple II gained widespread recognition for its user-friendly interface, which set it apart from competing systems. It became a popular choice for businesses, schools, and individuals.
2.2 The Launch of the Macintosh In 1984,
Apple made a significant breakthrough with the launch of the Macintosh. The Macintosh introduced a graphical user interface (GUI) and a mouse, making computers more accessible and intuitive. It revolutionized the way people interacted with computers and laid the foundation for future Macintosh models.
2.3 Impact on the Computer Industry
The Apple II and Macintosh played a crucial role in shaping the computer industry. They set new standards for design, ease of use, and innovation. The Macintosh, in particular, inspired a generation of designers, artists, and creative professionals, fostering a loyal following that persists to this day.
- The Wilderness Years and the Triumphant Return of Steve Jobs
3.1 Turmoil and Internal Conflicts In the late 1980s and throughout the 1990s, Apple faced numerous challenges. Internal conflicts, leadership changes, and a lack of product innovation led to declining sales and a loss of market share. The company struggled to find its direction and maintain its position in the competitive tech industry.
3.2 Steve Jobs’ Comeback In 1997, Apple acquired NeXT, a company founded by Steve Jobs during his time away from Apple. Jobs returned to Apple as interim CEO and soon took on a permanent role. His return marked a turning point for the company, as he brought a renewed focus on innovation, design, and user experience.
3.3 The Revival of Apple’s Culture Under Jobs’ leadership, Apple underwent a significant transformation. He streamlined Apple’s product lineup, emphasizing simplicity and elegance. The release of the iMac in 1998 marked the beginning of Apple’s resurgence, with its colorful design and emphasis on ease of use. This was followed by a series of successful products that reestablished Apple’s place in the industry.
- The iPod Revolutionizes Music Technology
4.1 Introduction of the iPod In 2001, Apple introduced the iPod, a portable music player that would revolutionize the way we listen to music. The iPod combined a sleek design, a user-friendly interface, and the ability to store thousands of songs. It seamlessly integrated with iTunes, Apple’s digital media software, creating a complete ecosystem for managing and enjoying music.
4.2 iTunes and the Digital Music Revolution Accompanying the iPod was iTunes, a platform that allowed users to purchase, organize, and synchronize their music library. iTunes disrupted the music industry, offering a legal and convenient way to obtain music in the era of digital piracy. It laid the groundwork for the shift from physical CDs to digital downloads and streaming.
4.3 Cultural Impact and Industry Transformation The iPod’s impact extended beyond its technological advancements. It became a cultural phenomenon, influencing fashion, popularizing white earphones, and fueling the growth of the digital music era. The success of the iPod propelled Apple’s brand recognition and set the stage for future innovations.
- The iPhone: Redefining the Smartphone Industry
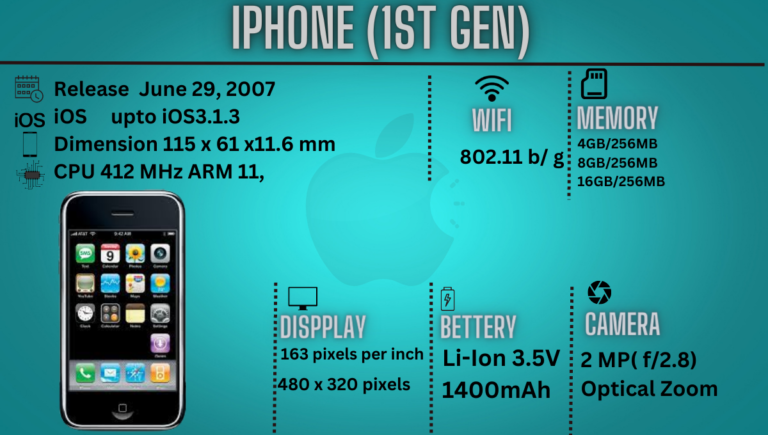
5.1 Unveiling the First iPhone In 2007, Apple unveiled the iPhone, a revolutionary device that combined a mobile phone, internet communicator, and iPod into one sleek package. The iPhone introduced a multi-touch interface, intuitive gestures, and a rich app ecosystem. It set a new standard for smartphones, challenging the industry’s status quo.
5.2 The App Store and Mobile App Revolution With the introduction of the App Store in 2008, Apple democratized software development, allowing third-party developers to create and distribute apps for the iPhone. This led to an explosion of innovation, with apps transforming various aspects of our lives, from communication and entertainment to productivity and health.
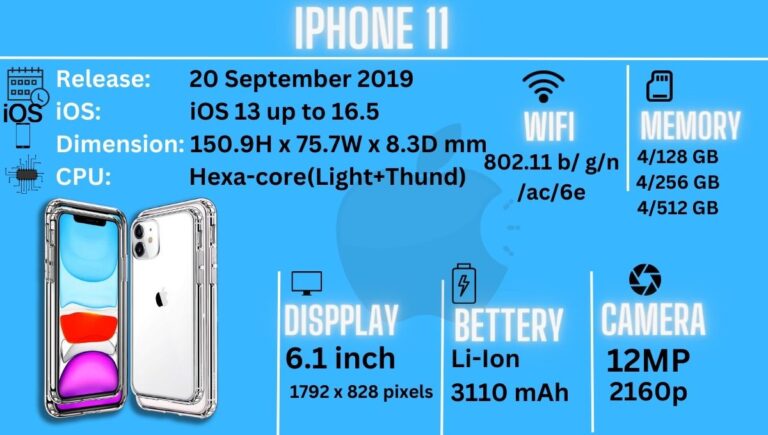
5.3 Shaping the Modern Smartphone Landscape The iPhone’s success had a profound impact on the smartphone industry. It compelled competitors to rethink their strategies, driving advancements in touchscreens, cameras, and mobile operating systems. The iPhone’s influence extended beyond technology, shaping consumer behavior, social interactions, and the way we access information.
- The iPad: Introducing a New Era of Tablets
6.1 The Launch of the iPad In 2010, Apple introduced the iPad, a tablet device that filled the gap between smartphones and laptops. The iPad offered a larger screen, a touch-centric interface, and a wide range of apps optimized for the tablet form factor. It aimed to revolutionize mobile computing and create new possibilities for content consumption and creation.
6.2 Transforming Industries and Use Cases The iPad had a profound impact on industries such as education, healthcare, and retail. It revolutionized classroom learning, enabling interactive and personalized education experiences. In healthcare, the iPad found applications in medical records, patient care, and diagnostics. Additionally, the iPad transformed the retail industry by providing a platform for mobile point-of-sale systems and enhancing customer engagement.
6.3 The Evolution of the iPad Lineup Over the years, the iPad lineup expanded to include various models and sizes, each catering to specific needs and user preferences. The introduction of features like Apple Pencil support and powerful processors further enhanced the iPad’s capabilities, positioning it as a versatile tool for productivity, creativity, and entertainment.
- Apple’s Ecosystem: Integration and Seamless User Experience
7.1 Building an Interconnected Ecosystem One of Apple’s key strengths lies in its 7.1 Building an Interconnected Ecosystem One of Apple’s key strengths lies in its interconnected ecosystem, where devices, software, and services seamlessly integrate to provide a unified user experience. This ecosystem includes products like Mac computers, iPhones, iPads, Apple Watches, and Apple TVs, all designed to work together effortlessly.
7.2 The Power of Synergy: Devices, Software, and Services Apple’s ecosystem thrives on the synergy between its devices, software, and services. Users can easily transition between different Apple devices, with features like Handoff allowing them to start a task on one device and seamlessly continue on another. iCloud keeps files, photos, and data in sync across devices, ensuring a consistent experience.
7.3 Fostering Customer Loyalty and Retention The strength of Apple’s ecosystem lies in its ability to create a seamless and integrated user experience. By offering a range of complementary devices and services, Apple enhances customer loyalty and retention. Users who become part of the Apple ecosystem often find it difficult to switch to other platforms due to the convenience and integration they enjoy.
- Innovations Beyond Devices: Apple’s Services and Initiatives
8.1 iTunes, App Store, and Apple Music Apple’s services have played a crucial role in its success. iTunes revolutionized the way we purchase and manage digital media, providing a legal and convenient platform for music, movies, TV shows, and more. The App Store transformed the mobile app landscape, creating a vibrant marketplace for developers and users. Apple Music, launched in 2015, brought a new era of music streaming and personalized recommendations to users.
8.2 Apple Pay and Apple Card In recent years, Apple has expanded its services to include financial products. Apple Pay allows users to make secure, contactless payments with their Apple devices, while Apple Card offers a digital and physical credit card with enhanced privacy and rewards programs. These services further integrate Apple’s ecosystem into users’ daily lives.
8.3 Sustainability and Environmental Initiatives Apple is committed to sustainability and has made significant efforts to reduce its environmental impact. The company operates on renewable energy, with data centers and offices powered by renewable sources. Apple has also focused on recycling and material sourcing to minimize waste and promote responsible manufacturing practices.
- Apple’s Ongoing Innovations and Future Endeavors
9.1 Apple Watch: Pioneering Wearable Technology The Apple Watch, introduced in 2015, has emerged as a leader in the wearable technology market. It combines fitness tracking, health monitoring, communication, and smartwatch functionality into a single device. With each new generation, Apple enhances the Watch’s capabilities, making it an indispensable companion for many users.
9.2 HomePod and AirPods: Transforming Audio Experiences Apple’s foray into the audio market includes the HomePod smart speaker and the AirPods wireless earbuds. The HomePod delivers high-quality sound and integrates with Apple’s ecosystem for seamless home automation. Meanwhile, AirPods revolutionized the wireless earbud market, offering convenience and superior audio quality.
9.3 Emerging Technologies: AR, Machine Learning, and More Apple continues to invest in emerging technologies, including augmented reality (AR) and machine learning. With ARKit, Apple’s AR platform, developers can create immersive AR experiences on Apple devices. Machine learning is integrated into various aspects of Apple’s ecosystem, from Siri’s intelligence to camera enhancements and personalized experiences.
- Conclusion: Apple’s Impact and Continued Dominance
The history of Apple Inc. is a testament to the power of vision, innovation, and user-centric design. From its humble beginnings in a garage, Apple has consistently pushed the boundaries of technology and transformed industries. The company’s iconic products, such as the Macintosh, iPod, iPhone, and iPad, have become cultural touchstones and have shaped the way we interact with technology.
Apple’s ecosystem, with its seamless integration of devices, software, and services, has created a loyal customer base and fostered a sense of brand loyalty. As Apple continues to innovate and expand into new areas, such as wearables, services, and emerging technologies, it is well-positioned to maintain its dominance in the global tech industry.
Looking ahead, Apple’s commitment to design excellence, user experience, and environmental sustainability will continue to drive its success. The story of Apple Inc. serves as an inspiration for aspiring entrepreneurs and reminds us of the transformative power of innovation and the impact a single idea can have on the world.